한약은 감염 후 기침 치료에 유용하고 안전하다는 논문(일본)
Antitussive effect of bakumondoto a fixed kampo medicine (six herbal components) for treatment of post-infectious prolonged cough: controlled clinical pilot study with 19 patients
Kazunori Irifune 1, Hironobu Hamada, Ryoji Ito, Hitoshi Katayama, Akira Watanabe, Aki Kato, Seigo Miyoshi, Naohiko Hamaguchi, Ryo Toyozawa, Sachiko Hamaguchi, Masahiro Abe, Kazutaka Nishimura, Jitsuo Higaki
Affiliations expand
PMID: 21514123 DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.02.017
Abstract
Bakumondoto (TJ-29) is a traditional herbal medicine that has been used in Japan for the treatment of bronchitis, bronchial asthma, and cough. This study investigated the effect of TJ-29 for the treatment of post-infectious prolonged cough. We performed a multicenter randomized controlled trial treating patients without (group A, n=11) or with TJ-29 (group B, n=8) for a total of 2 weeks using a beta 2 stimulant as the basal agent. Efficacy and safety were compared by a cough diary, VAS and sleeping questionnaire. At 4 and 5 days after treatment, the cough score of group B showed significant improvement compared with group A, demonstrating an early antitussive effect. At the assessment 2 weeks after treatment start, both groups showed similar levels of improvement in the cough score. No significant difference was observed in the VAS and the sleeping questionnaire items. In conclusion, oral TJ-29 administration could be useful and safe for the treatment of post-infectious prolonged cough.
한약이 호흡기에서 일어나는 염증과정을 억제한다는 논문(중국)
Xia-bai-san inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and nuclear factor-kappa B in human lung cells
Kuo-Hua Lee 1, Ming-Hsien Yeh, Shung-Te Kao, Che-Ming Hung, Bor-Chyuan Chen, Ching-Ju Liu, Chia-Chou Yeh
Affiliations expand
PMID: 19454309 DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.05.007
Abstract
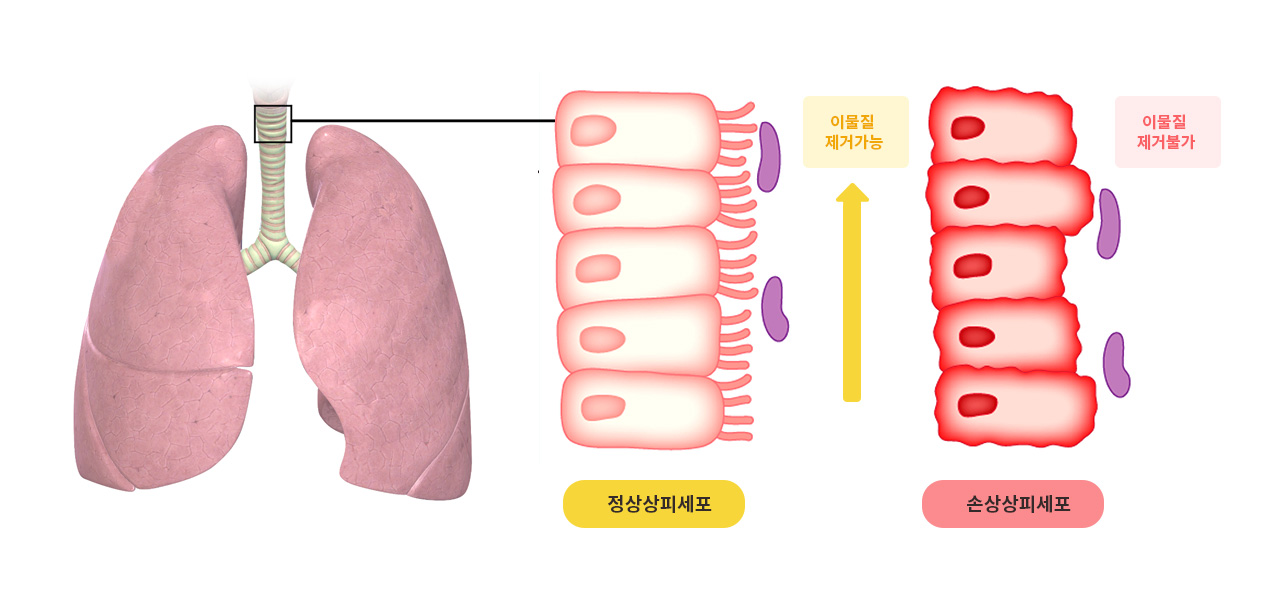
Xia-bai-san (XBS) is a traditional Chinese medicine that has been used clinically for centuries in Asian countries to treat some types of common cold and asthma-like diseases similar to infantile pneumonia and childhood bronchitis. In previous studies, XBS was found to suppress the inflammatory process induced in lungs of mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Purpose: The present study was undertaken to examine the effects of XBS on LPS-inducible production of inflammatory cytokines, up-regulation of intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and activation of nuclear factor NF-kappaB in cultured human lung cells.
Principal results: Extracts of four raw herbs (Cortex mori, Cortex lycii, Radix glycyrrhizae, and Fructus oryzae) were used to prepare the decoction. XBS decreased the histological damage and up-regulation of ICAM-1 observed in lungs of mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In cultured human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells, XBS and its components Morus alba and Glycyrrhiza uralensis suppressed the up-regulation of IL-8 and ICAM-1 in response to LPS. Production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8 by LPS-treated human THP-1 monomyelocytes was also suppressed by XBS. A549 cells expressed ICAM-1 in response to medium from LPS-treated THP-1 cells; expression was decreased by XBS. The adhesion of THP-1 cells to LPS-treated A549 cells were inhibited in the presence of XBS. Activation of NF-kappaB by LPS in A549 cells was suppressed by XBS, Morus alba, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis through inhibition of IkappaB phosphorylation; the concentrations at which suppression occurred were identical to those at which production of inflammatory cytokines and up-regulation of ICAM-1 were inhibited.
Major conclusions: These findings support the hypothesis that XBS, Morus alba, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis inhibit the inflammatory process in lung tissue through suppression of the IkappaB signaling pathway. XBS may prove helpful in the management of asthma, various allergic disorders, sepsis, or any other condition associated with pulmonary inflammation.

 김00 38세(여)
김00 38세(여)
 박00 16세(여)
박00 16세(여)




















 이사무 선생의 진료실에서
이사무 선생의 진료실에서


