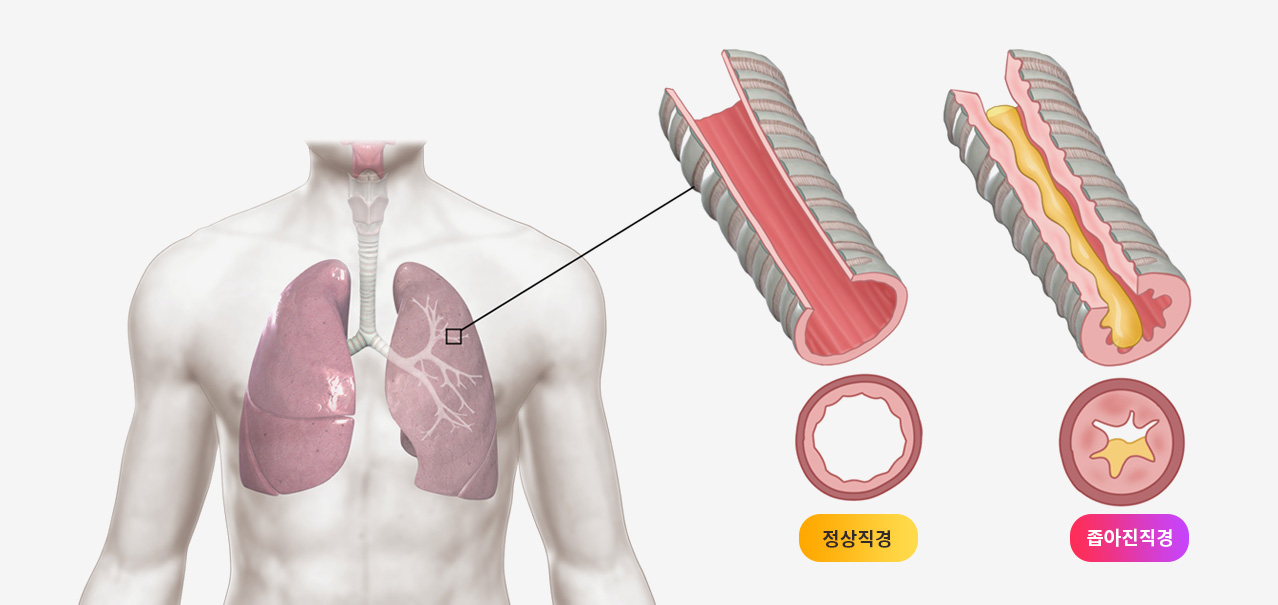
이러한 기침이형천식에 한약치료가 도움이 될 수 있는지 살펴보겠습니다.
2635명이 참가한 총 25개의 무작위대조시험에서 양약인 몬테루카스트와 여러 한약의 효과를 비교한 논문. 몬테루카스트와 비교하여 한약이 더 효과적이었고, 부작용이 적었다는 내용
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine for cough variant asthma: A network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Author links open overlay panelChenxiaoBaiLiwenWangDiJiangOuChen
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2019.101028Get rights and content
Abstract
Introduction
Cough variant asthma (CVA) can lead to chronic cough or typical asthma. Though western medications have shown benefit, many patients do not achieve long term effects. Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) has been used for patients with CVA, however its benefit is unclear. This review aimed to evaluate the efficacy of different CHM for patients with CVA using network meta-analysis.
Methods
Embase, Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI and WanFang databases were searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy of CHM with Montelukast (western medicine). Studies selection, data extraction, and quality evaluation were independently conducted by two reviewers. Network meta-analysis was performed to rank different therapies according to efficacy and adverse rates.
Results
A total of 25 RCTs involving 2635 participants were included in the study. The study indicated that compared with Montelukast, the efficacy rate of CHM was significantly higher (Odd ratio (OR) = 4.13; 95% credible intervals (CI): 3.29–5.20). Only 8 RCTs reported the adverse reactions. The study suggested fewer adverse effects of CHM (OR = 0.26; 95% CI: 0.16-0.43) when compared with Montelukast. In the network meta-analysis, Suhuang Zhike Capsule (SZC) + Montelukast, Xiaoqinglong Decoction (XQLD) + Montelukast, Zhisousan + Montelukast and ephedra soup + Montelukast were most likely to take effect in CVA patients, while SZC + Montelukast and Montelukast were more likely to have adverse effects.
Conclusions
Compared with Montelukast, CHMs were more effective and had less adverse effects in the treatment of CVA.
그런가 하면 한약이 기침이형천식에 어떤식으로 작용하는지 메커니즘을 설명한 연구도 있습니다.
한약이 기침이형천식치료에 좋은 효과를 내는 메커니즘 연구
기도과민반응 지표인 IL4,IL13를 감소시키고 과민체질인 사람에게 높은 NGF단백질 수치를 내려주고, 천식과 같은 알러지증상에서 주요역할을 담당하는 CGRP 수준을 감소시키는 효과가 있으며 TRP채널을 조절한다.
Effect of San'ao decoction with scorpio and bombyx batryticatus on CVA mice
model via airway inflammation and regulation of TRPA1/TRPV1/TRPV5 channels
Pengli Wang 1, Erxin Shang 2, Xinsheng Fan 3
Affiliations expand
PMID: 32890712 DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113342
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Cough variant asthma (CVA) is characterized with its long-lasting cough symptom on clinic. The mechanism of CVA is related to chronic persistent airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, etc. The traditional Chinese prescription has achieved good curative effect on CVA treatment through reducing cough counts, decreasing airway hyperresponsiveness and alleviating airway inflammation. The mechanism is associated with reducing IL4, IL-13, NGF and CGRP levels, as well as down-regulating TRPA1/TRPV1/TRPV5 channels in both lung and brain tissues.
Aim of the study: The Chinese prescription, San'ao decoction with scorpio and bombyx batryticatus (SSB), is well known in treating cough in asthmatic patients. In this study, the anti-tussive and anti-asthmatic role of SSB, as well as its mechanism on CVA mice model were explored and evaluated via alleviating airway inflammation and regulation of TRP channels.
Materials and methods: The major chemical components in SSB were detected and analyzed by UPLC-QTOF-MS under an optimized chromatographic and MS condition. 60 BALB/c mice were randomly divided into six groups: normal group, model group, dexamethasone group (0.1178 mg/kg/d), SSB high dose group (9.74 g/kg/d), SSB middle dose group (4.87 g/kg/d) and SSB low dose group (2.435 g/kg/d). The cough variant asthma mice model was established by ovalbumin sensitization and challenge. The protective role of SSB on CVA mice model was studied through inducing cough counts by capsaicin, assessing inflammatory cells in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), measuring airway responsiveness, detecting histopathological changes in lung tissues, analyzing cytokines and neuropeptides levels in BALF, as well as examining the mRNA and protein expressions of TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPV5 in both lung and brain tissues.
Results: 17 signal peaks of the chemical components in SSB were identified by using UPLC-QTOF-MS. SSB (especially the high dose and middle dose), showed significantly effects on mice model by reducing mice cough counts (P < 0.01), decreasing eosinophil (EOS) counts in blood (P < 0.01) and inflammatory cell numbers in BALF (P < 0.01), decreasing airway hyperresponsiveness (P < 0.05), reducing the levels of IL-4 (P < 0.05), IL-13 (P < 0.01), NGF (P < 0.01) and CGRP (P < 0.01) in BALF, as well as down regulating the mRNA and protein expressions of TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPV5 in both lung and brain tissues (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: SSB showed anti-tussive and anti-asthmatic effects on cough variant asthma mice model by reducing cough counts, improving lung function, alleviating lung injury and airway inflammation. The mechanism of SSB might be associated with the regulation of cytokines and neuropeptides in BALF, as well as the regulation of TRPA1, TRPV1, TRPV5 channels in both lung and brain tissues.
Keywords: Airway inflammation; Cough variant asthma; San'ao decoction with scorpio and bombyx batryticatus; TRPA1/TRPV1/TRPV5 channels.




















 이사무 선생의 진료실에서
이사무 선생의 진료실에서


