해외 논문 하나를 살펴봅시다.
1355명을 대상으로 한약치료가 후비루증후군에 어떤 효과를 가져다 줄 수 있는지 연구한 논문입니다.
Chinese Medicinal Herbs in the Treatment of Upper Airway Cough Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Randomized, Controlled Trials
Hongli Jiang, Wei Liu, Guanhong Li, Tao Fan, Bing Mao
Altern Ther Health Med. 2016 Mar;22(3):38-51.
Abstract
Context Upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), previously called postnasal drip syndrome (PNDS), has been considered universally to be one of the most common causes of chronic cough. As an important part of complementary and alternative therapy, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has found an exact curative therapy for chronic cough through clinical practice for thousands of years. Objective The aim of the current review was to investigate systematically the beneficial and adverse effects of Chinese medicinal herbs (CMH) in the treatment of UACS. Design The research team performed searches in 11 main databases from respective inception to October 31, 2015, supplemented with manual retrieval of other data. Only randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) reporting on the effectiveness of CMH in patients with UACS were included. Descriptive and quantitative data on the studies' designs, population demographics, interventions, outcomes, and methodological quality were extracted and tabulated. Methodological quality was assessed using the Cochrane risk-of-bias system and the quality of the evidence was evaluated using the Grades of Recommendation Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system. Participants The reviewed studies included 1355 participants-720 in the CMH groups and 635 in the control groups-of both genders, from various professional and ethnic groups, and with a wide range of ages. They all had a duration of cough symptoms of longer than 8 wk and a clinical diagnosis of chronic cough induced by UACS that was supported by appropriate physical findings.
Outcome Measures The primary outcomes included (1) TCM recovery rate and (2) TCM cough symptom score. TCM's curative effect was calculated as the cumulative percentage of the symptom-score reduction (PSSR), estimated between baseline and postintervention. The cough symptom scores were graded according to the Chinese Criteria Guiding Principle of Clinical Research on New Drugs of TCM, with the scores being classified into 4 grades. Those scores ranged from 0-3 (ie, 0, 1, 2, 3, respectively), or 0-9 (ie, 0, 3, 6, 9, respectively), with the higher scores signifying a more frequent and severe cough. Results A total of 16 studies that had been published in Chinese journals was ultimately identified for the review. The majority of methodological judgments demonstrated an unclear risk of bias. A meta-analysis was conducted using a random effects model due to the poor homogeneity of the studies. Compared with Western medicine (WM), patients in both the CMH groups and the integrated therapy groups showed (1) a higher TCM recovery rate; (2) better relief of primary symptoms, including cough and postnasal dripping; (3) a reduction in physical signs, including the cobblestone appearance of the oropharyngeal mucosa or mucus in the oropharynx; and (4) a lower risk of cough relapse. No severe adverse events occurred in either group.
Conclusions CMH may be a safe and effective alternative for the treatment of UACS. The study highlighted the paucity of reliable clinical evidence for CMH and the need for RCTs of higher quality in the future.
일부를 발췌해보면
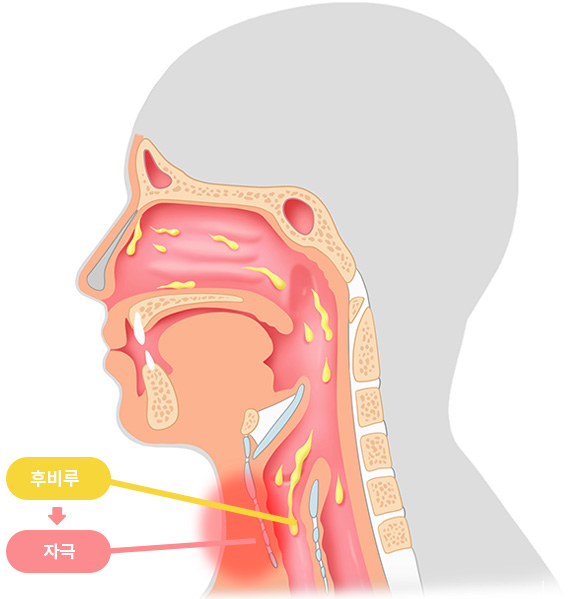
후비루 증후군에 한약치료를 하면
better relief of primary symptoms, including cough and postnasal dripping
기침을 포함한 일차 증상의 더 나은 완화를 가져다 주고
a reduction in physical signs, including the cobblestone appearance of the oropharyngeal mucosa or mucus in the oropharynx
구인두 점막이나 구인두 점액의 조약돌 모양을 포함한 신체적 징후를 감소시키고
a lower risk of cough relapse
기침 재발 위험을 감소 시키고
No severe adverse events occurred in either group
심각한 부작용은 발생하지 않았다
safe and effective alternative for the treatment of UACS
한약이 상기도기침증후군(후비루증후군)에 안전하고 효과적일 수 있다
후비루증후군에 한약이 역할을 할 수 있음을 충분히 기대할 수 있게 하는 논문입니다.
이런 한약의 우수성은 어떤 한의사를 만나느냐에 따라 더욱 효과가 발휘됩니다. 아무래도 한의사도 집중해서 연구하고 치료하는 분야가 다르기 때문에 그렇습니다.





















 이사무 선생의 진료실에서
이사무 선생의 진료실에서


