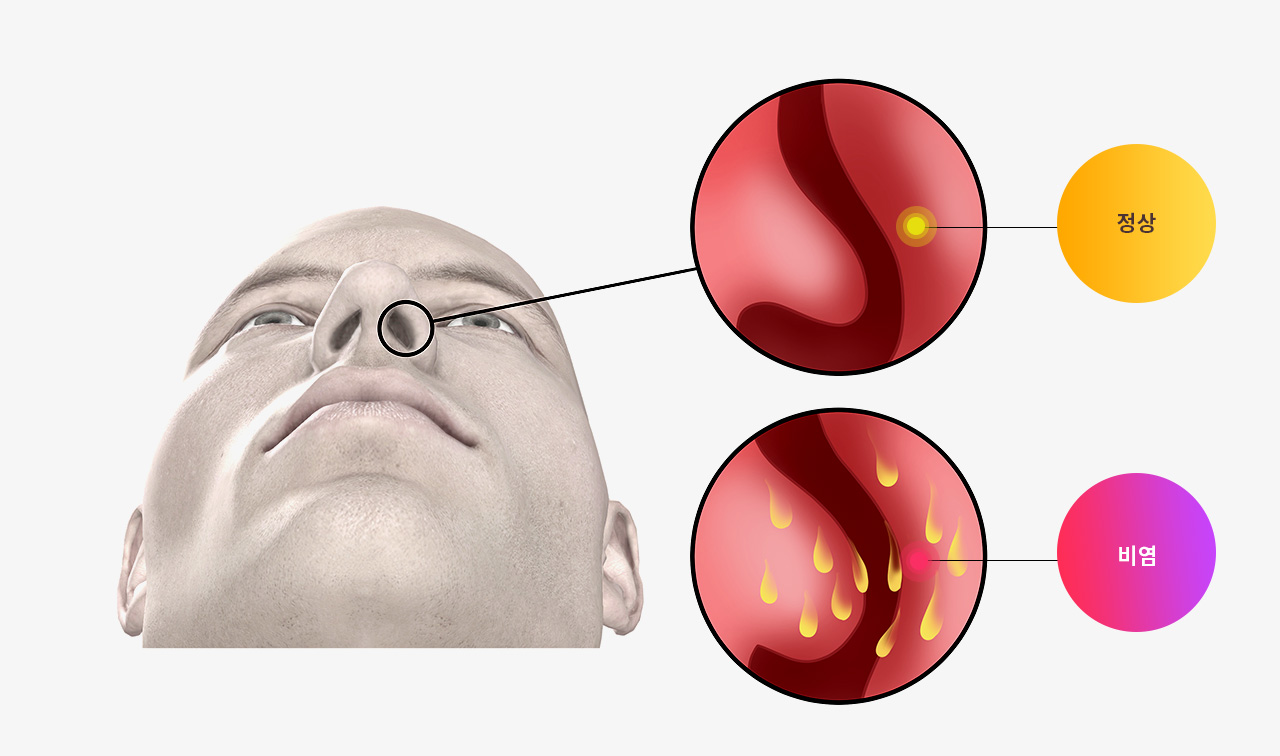
다년성 알러지비염 환자를 위한 한약의 효능
Efficacy of Bimin decoction for patients with perennial allergic rhinitis: an open-label non-inferiority randomized controlled trial
Jingyi Zhao 1 , Xinyu Yan 1 , Jianqing Gai 1 , Jinshuai Han 1 , Hong Zhang 1 , Hui Luo 1 , Shaoting Huang 1 , Junge Wang 2
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common allergic disease. It affects people worldwide and traditional Chinese medicine is becoming popular among AR patients because it has a definite clinical effect and there are few adverse reactions. Lung qi deficiency and cold syndrome (LQDCS) is a frequent type of AR, and the Chinese herbal medicine bimin decoction (BMD) is prescribed for it. This study compared the clinical efficacy of BMD for AR patients with LQDCS to the conventional medicine loratadine and fluticasone nasal spray.
Methods: The study was an open-label non-inferiority randomized controlled trial. A total of 108 AR patients with LQDCS aged 19 to 60 were randomly allocated in a 1:1 ratio to the BMD group or the control group by the central computer system in Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2017 to April 2018. In total, 98 participants completed the study (BMD group n = 51 and control group n = 47). Patients in the BMD group received BMD while those in the control group received fluticasone nasal spray and loratadine tablets for 4 weeks. The primary outcome was the change in the Total Nasal Symptom Score (TNSS) between the baseline and the end of treatment. Changes in the Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire (RQLQ), nasal resistance, and acoustic rhinometry parameters were secondary outcomes. All side effects due to the treatments were recorded.
Results: After the 4-week treatment, the total TNSS was significantly reduced in both groups compared to the baseline (P < 0.05). No significant between-groups differences were observed for changes in TNSS scores [- 0.298 (95% confidence interval -0.640 to 0.140)], which was within the defined non-inferiority margin. RQLQ in both groups decreased significantly (P < 0.001) from baseline, though a more obvious reduction was observed for the BMD group (P < 0.001). There were no significant differences in nasal resistance, nasal volume, or nasal minimum cross-sectional area between groups after treatment (P> 0.05).
Conclusions: These findings indicate that BMD helps relieve the symptoms of perennial AR and improves rhinitis-related quality of life. Our study indicates that BMD is non-inferior to loratadine tablets and fluticasone nasal spray for AR patients with LQDCS.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR-INR-16010063. Registered on 2 December 2016.
Keywords: Clinical efficacy; Perennial allergic rhinitis; Randomized controlled trial; Traditional Chinese medicine.
본 논문에서 한약이 다년성 알러지비염의 증상을 완화하고 비염 관련 삶의 질을 향상시키는데 도움이 된다는 것을 보여줍니다.
이 연구에서는 한약이 양약 로라타딘(제품명:클라리틴), 코 스프레이(제품명:아바미스나잘 스프레이)보다 효능이 떨어지지 않는다는 것을 보여줍니다.
알레르기 반응에 대한 한약의 효과
Effect of Shin'iseihaito on murine allergic reaction induced by nasal sensitization.
Minami M1, Konishi T2, Jiang Z3, Arai T3, Makino T2.
Author information
1Department of Bacteriology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagoya City University, 1 Kawasumi, Mizuho-ku, Nagoya, Japan.2Department of Pharmacognosy, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Nagoya City University, 3-1 Tanabe-Dori, Mizuho-ku, Nagoya, Japan.3R&D Center, Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., 4-10 Doshomachi 4-chome, Chuo-ku, Osaka, Japan.
Abstract
Shin'iseihaito (Magnolia Flower Lung-Clearing Decoction; xīn yí qīng fèi tāng), a formula of traditional Japanese kampo medicine ( rì běn hàn yī) and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM; zhōng yī), has been used for the treatment of chronic sinusitis. The objective of this study was to evaluate the anti-allergic effect of shin'iseihaito on murine allergic reaction induced by nasal sensitization using ovalbumin (OVA) as an antigen. Extract of shin'iseihaito (SSHT) could reduce the eosinophil, serum IgE and interleukin (IL)-4 levels, while increased the interferon (IFN)-γ levels in allergic mouse. Furthermore, allergic-murine serum treated with SSHT could not activate passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) reaction in murine model. Thus, our study showed that SSHT may possess anti-allergic activity. We suggested that SSHT may contribute to inhibit the exacerbation of allergic reaction induced by nasal sensitization
(J Tradit Complement Med. 2015 Jun 21;6(3):252-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2015.06.001. eCollection 2016 Jul.)
한약이 호산구와 IL-4 (알러지를 유발하는 사이토카인)을 감소시키고 면역조절을 담당하는 IFN-γ 수치를 증가시킵니다.




















 이사무 선생의 진료실에서
이사무 선생의 진료실에서


