한약이 폐섬유증을 억제할 수 있다는 논문(중국)
The ethical Kampo formulation Sho-seiryu-to (TJ-19) prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
Yang CQ1, Sun PY, Ding DZ, Moriuchi H, Ishitsuka Y, Irikura M, Irie T.
Author information
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Yanbian University, Jilin Prov., Yanji 133000, China.
Abstract
The effects of Sho-seiryu-to (TJ-19), an ethical Kampo formulation, on bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats was examined. Pulmonary fibrosis was induced by intratracheal instillation of a single dose of BLM (5 mg/kg). The TJ-19 used consisted of at least 21 constituents, as determined by three-dimensional HPLC analysis, and was administered orally twice a day at a dose of 1.5 g/kg until the end of the study period. Changes in general appearance and body weight were monitored. Twenty-eight days after BLM instillation, the animals were sacrificed and the study parameters were measured. TJ-19 attenuated the loss in body weight, increase in lung/body weight ratio and concentration of hydroxyproline and malondialdehyde in the lung tissues induced by BLM administration. TJ-19 also prevented BLM-induced fibrotic changes in the lung histology. These protective effects of TJ-19 were observed when administration was started 1 week before and simultaneously with the instillation of BLM. These results suggest that TJ-19 has prophylactic potential against BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis, and may therefore be a promising drug candidate and medicinal resource for preventing BLM-induced and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
(Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(8):1438-42)
한약이 항산화 항염증 활성을 가지고 있으며 콜라겐형성을 억제하여 폐섬유 손상을 막을 수 있다는 논문(대만)
A kampo medicine, Yin-Chiao-san, prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury in rats.
Yen FL1, Wu TH, Liao CW, Lin CC.
Author information
Graduate Institute of Pharmaceutical Science, College of Pharmacy, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Abstract
Yin-Chiao-San (YCS), a kampo medicine, is widely used for patients with pulmonary disease and was applied for the treatment of SARS in Asia countries in 2003. For this reason, the present study investigated the preventive effect of YCS on bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis (PF) in rats. Animals were divided into four groups: (1) saline control group; (2) BLM-induced group, in which 15 mg/kg BLM was intraperitoneally injected three times per week for a period of 5 weeks; (3) BLM + vitamin E (10 mg/kg/day) as a positive group; (4) and BLM + YCS (1000 mg/kg/day). After 35 days, the rats were anesthetized, killed and then the lungs and bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALFs) were collected. The attenuation of pulmonary fibrosis was estimated according to the lung index, malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase (CAT), hydroxyproline (HP) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) level in lung tissue and BALF. The serial sections of lung were stained with haematoxylin-eosin and Masson trichrome for histopathological observation of pulmonary fibrosis. The results indicated that YCS significantly reduced the lung index, MDA, HP and TNF-alpha, but YCS significantly enhanced the CAT level when compared with the BLM-induced group (p < 0.05). Additionally, the BLM group displayed severe histopathological change in the lung tissue, but YCS treatment could attenuate the BLM-induced PF. In conclusion, the results demonstrated that YCS possesses antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities and also inhibited collagen formation. Thus, YCS exhibited a preventive effect in BLM-induced PF and it is suggested that YCS may be applied to attenuate the side effects of BLM in chemotherapy
(Phytother Res. 2007 Mar;21(3):251-8.)
한약재가 폐 섬유증 관련 염증 유전자뿐만 아니라 근섬유 아세포 활성화 및 콜라겐 침착과 관련된 유전자도 조절하는 것으로 나타났다는 논문(중국)
Ability to Suppress TGF-β-Activated Myofibroblast Differentiation Distinguishes the Anti-pulmonary Fibrosis Efficacy of Two Danshen-Containing Chinese Herbal Medicine
(Prescriptions
Rui Shao 1 2, Fu-Jiang Wang 1 2, Ming Lyu 1 2, Jian Yang 1 2, Peng Zhang 1 2, Yan Zhu 1 2)
Affiliations expand
PMID: 31105564 PMCID: PMC6491955 DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00412
Free PMC article
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating lung disease with limited treatment options. It also leads to progressive respiratory failure, which subsequently affects the heart functionality, a pathological heart-lung interaction increasingly noticed and defined as pulmonary-heart disease (PHD). Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) theory for treating "phlegm-stasis cementation syndrome" may suggest a possibility of treating PHD complication with Chinese medicine prescriptions previously used for cardiovascular diseases.
Methods: Here, we evaluate the efficacies of two compound Chinese medicine prescriptions, Danlou prescription (DLP) and Danhong prescription (DHP), which share a common herbal component, Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen), on pulmonary fibrosis. Severity grades of Bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary fibrosis were assessed by micro-Computerized Tomography (μCT) in accordance with the clinical evaluation standard. Lung pathological changes and collagen deposition were investigated by histopathology. Myofibroblast differentiation was assessed by immunohistochemistry of α-SMA and TGF-β receptor type II expression in situ. Network pharmacology analysis of the drug-target interaction in IPF progression for DLP or DHP was performed using Ingenuity® Pathways Analysis (IPA) system.
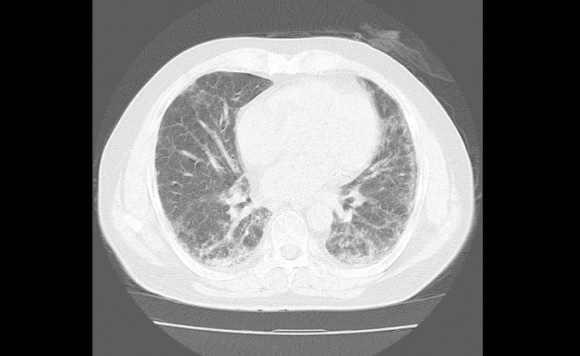
Results: We show that a non-invasive μCT effectively monitor and quantify BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis and its treatment efficacy by Chinese medicine prescription in rodents. In addition, although both containing Salvia miltiorrhiza, DLP but not DHP mitigates BLM-induced lung fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β signaling-activated myofibroblast differentiation and α-SMA expression in a mouse model. Core analysis by IPA revealed that DLP ingredients regulated not only pulmonary fibrosis related inflammatory genes but also genes associated with myofibroblast activation and collagen deposition.
Conclusion: This study suggests that a clinically efficacious cardiovascular Chinese herbal medicine (DLP) can be successfully repurposed to treat a lung disease in pulmonary fibrosis guided by TCM theory. Our comparative study between DLP and DHP demonstrated a critical requirement of suppressing both pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pathways for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, supporting that a multi-component prescription capable of "removing both phlegm and blood stasis" will better achieve co-protection of heart and lung in PHD.
Keywords: Danhong prescription; Danlou prescription; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; myofibroblast differentiation; pulmonary-heart disease.
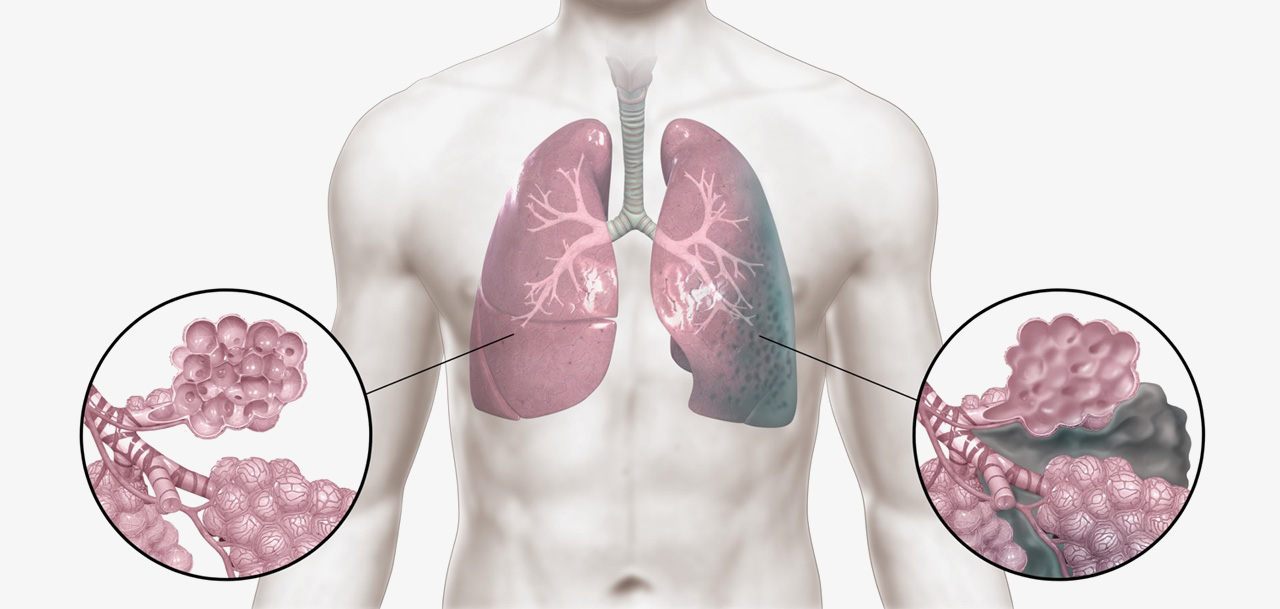
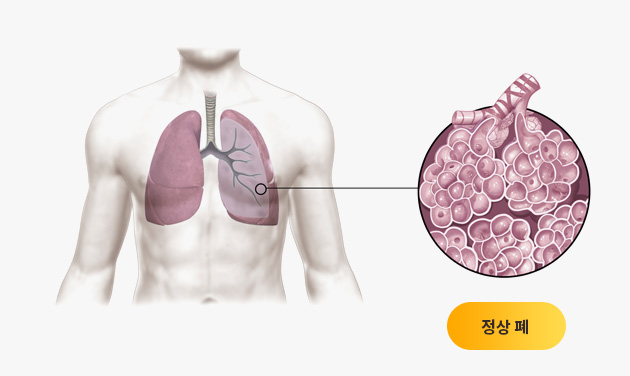
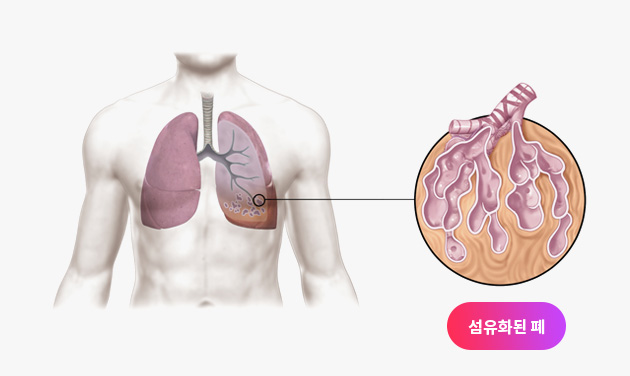
특발성폐섬유증과 같은 간질성폐질환은 예후가 좋지 못하다고 알려진 병입니다. 하지만 한약 치료를 통해 이 병을 극복하려는 노력이 진행되고 있습니다.





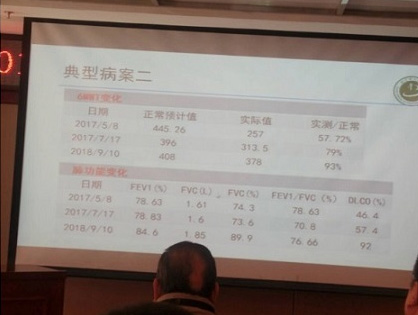





















 이사무 선생의 진료실에서
이사무 선생의 진료실에서


